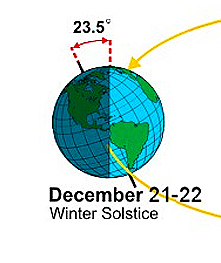
 December 21, 2018 Winter Solstice 2018 Observed (Northern Hemisphere) - The winter solstice (or hibernal solstice), also known as midwinter, is an astronomical phenomenon marking the day with the shortest period of daylight and the longest night of the year. It occurs when one of the Earth's poles has its maximum tilt away from the Sun. It happens twice yearly, once in each hemisphere. In the Northern Hemisphere this is the December solstice and in the Southern Hemisphere this is the June solstice. - Summer Solstice 2018 Observed (Southern Hemisphere)
December 21, 2018 Winter Solstice 2018 Observed (Northern Hemisphere) - The winter solstice (or hibernal solstice), also known as midwinter, is an astronomical phenomenon marking the day with the shortest period of daylight and the longest night of the year. It occurs when one of the Earth's poles has its maximum tilt away from the Sun. It happens twice yearly, once in each hemisphere. In the Northern Hemisphere this is the December solstice and in the Southern Hemisphere this is the June solstice. - Summer Solstice 2018 Observed (Southern Hemisphere)The axial tilt of Earth and gyroscopic effects of its daily rotation mean that the two opposite points in the sky to which the Earth's axis of rotation points (axial precession) change very slowly (at the current rate it would take just under 26,000 years to make a complete circle). As the Earth follows its orbit around the Sun, the polar hemisphere that faced away from the Sun, experiencing winter, will, in half a year, face towards the Sun and experience summer. This is because the two hemispheres face opposite directions along Earth's axis, and so as one polar hemisphere experiences winter, the other experiences summer. - Summer Solstice 2018 Observed (Southern Hemisphere)
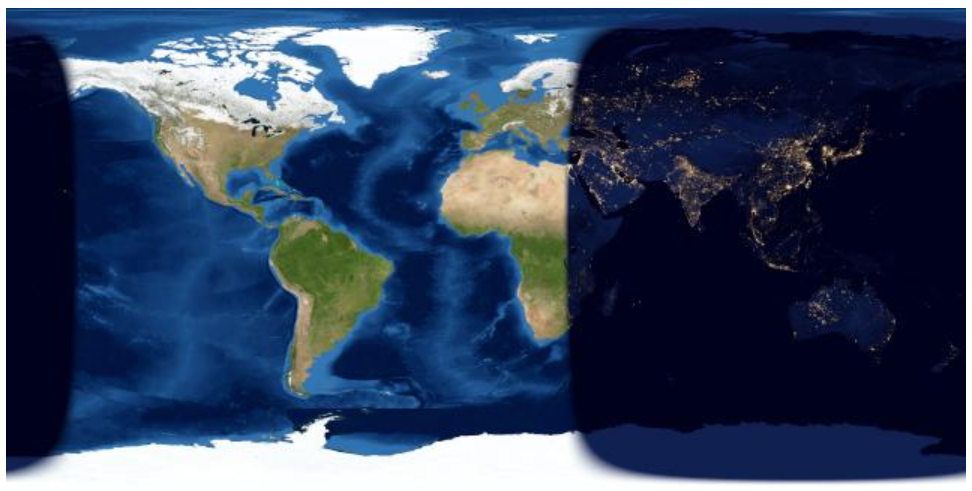 More evident from high latitudes, a hemisphere's winter solstice occurs on the day with the shortest period of daylight and longest night of the year, when the sun's daily maximum elevation in the sky is at its lowest.[1] Although the winter solstice itself lasts only a moment in time, the term sometimes refers to the day on which it occurs. Other names are "midwinter", the "extreme of winter" (Dongzhi), or the "shortest day". In some cultures it is seen as the middle of winter, while in others it is seen as the beginning of winter. In meteorology, winter in the Northern Hemisphere spans the entire period of December through February. - Summer Solstice 2018 Observed (Southern Hemisphere)
More evident from high latitudes, a hemisphere's winter solstice occurs on the day with the shortest period of daylight and longest night of the year, when the sun's daily maximum elevation in the sky is at its lowest.[1] Although the winter solstice itself lasts only a moment in time, the term sometimes refers to the day on which it occurs. Other names are "midwinter", the "extreme of winter" (Dongzhi), or the "shortest day". In some cultures it is seen as the middle of winter, while in others it is seen as the beginning of winter. In meteorology, winter in the Northern Hemisphere spans the entire period of December through February. - Summer Solstice 2018 Observed (Southern Hemisphere)The seasonal significance of the winter solstice is in the reversal of the gradual lengthening of nights and shortening hours of daylight during the day. The earliest sunset and latest sunrise dates differ from winter solstice, however, and these depend on latitude, due to the variation in the solar day throughout the year caused by the Earth's elliptical orbit (see earliest and latest sunrise and sunset). Worldwide, interpretation of the event has varied across cultures, but many have held a recognition of rebirth, involving holidays, festivals, gatherings, rituals or other celebrations around that time. - Summer Solstice 2018 Observed (Southern Hemisphere)